Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, raw numbers and spreadsheets are no longer enough to make sense of complex information. Businesses, analysts, and researchers are increasingly turning to interactive dashboards to visualise data and uncover actionable insights. These dashboards provide dynamic, user-friendly interfaces that allow stakeholders to interact with data in real-time—filtering, drilling down and drawing conclusions without needing advanced technical skills.
Streamlit has rapidly gained popularity for building such dashboards. Lightweight, Python-based, and incredibly easy to use, Streamlit allows data professionals to write just a few lines of code to transform their analyses into web apps that can be shared. This blog explores how Streamlit is revolutionising the dashboard creation process and why it is an essential tool in the modern data analytics toolkit.
What is Streamlit?
Streamlit is an open-source Python library for building web applications, specifically for machine learning modelling and data science projects. Unlike traditional web development frameworks that require knowledge of HTML, CSS, or JavaScript, Streamlit enables developers to create full-fledged, interactive dashboards using only Python.
Key features of Streamlit include:
- Simplicity: Create functional web apps with minimal code.
- Interactivity: Add widgets like sliders, dropdowns, and checkboxes to explore data dynamically.
- Speed: Real-time updates ensure fast user interaction without page reloads.
- Integration: Seamlessly works with popular Python libraries like Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, Plotly, and Scikit-learn.
Streamlit is particularly appealing to data analysts and data scientists who want to share insights and models without getting bogged down by front-end development.
Why Interactive Dashboards Matter in Data Analytics
Interactive dashboards offer a clear edge over static reports. They enable users to manipulate parameters, select time frames, apply filters, and explore various scenarios—all within a single interface.
Benefits include:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Users can slice and dice data instantly to answer specific business questions.
- Improved Communication: Visual representations make it easier for non-technical stakeholders to understand trends and patterns, enhancing their comprehension.
- Time Efficiency: Automates repetitive reporting tasks and allows real-time data monitoring.
- Accessibility: Dashboards can be shared as web applications or hosted in the cloud, providing global access without the need for installation.
In a landscape where quick, informed decisions are vital, the ability to explore data interactively is a game-changer.
Getting Started with Streamlit
Setting up Streamlit is straightforward, especially for users familiar with Python. Here is how you can get started:
Installation
Install Streamlit via pip:
pip install streamlit
Create a Python Script
Write your dashboard logic in a .py file. For example:
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
st.title(“Sales Dashboard”)
data = pd.read_csv(“sales_data.csv”)
st.dataframe(data)
Run the App
Launch the app in your browser:
streamlit run your_script.py
Add Interactivity
Enhance your dashboard with widgets like sliders:
year = st.slider(“Select Year”, 2015, 2024)
filtered_data = data[data[‘Year’] == year]
st.line_chart(filtered_data[‘Revenue’])
In just a few lines of code, you have built a live, interactive web app ready to share with your team.
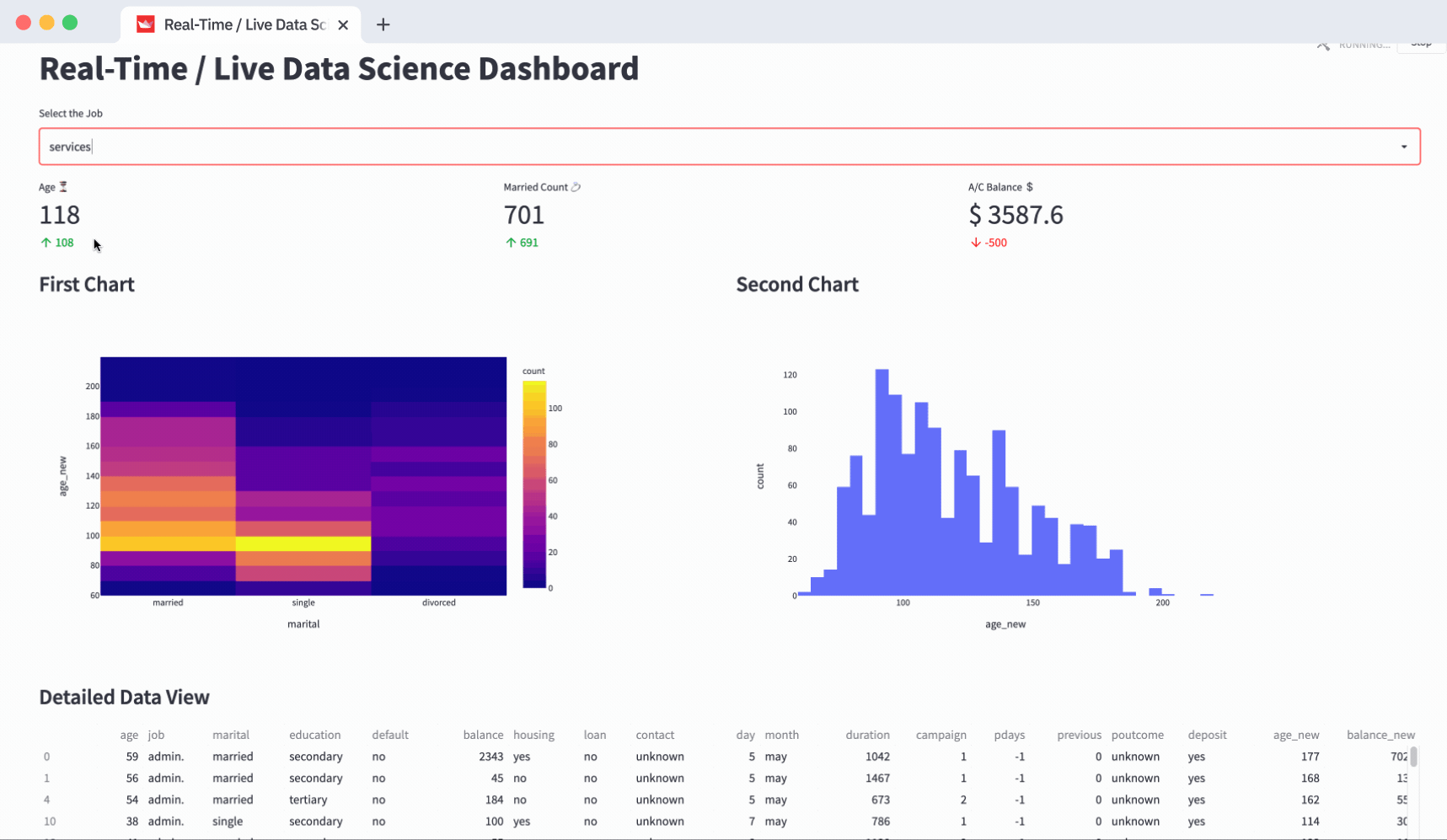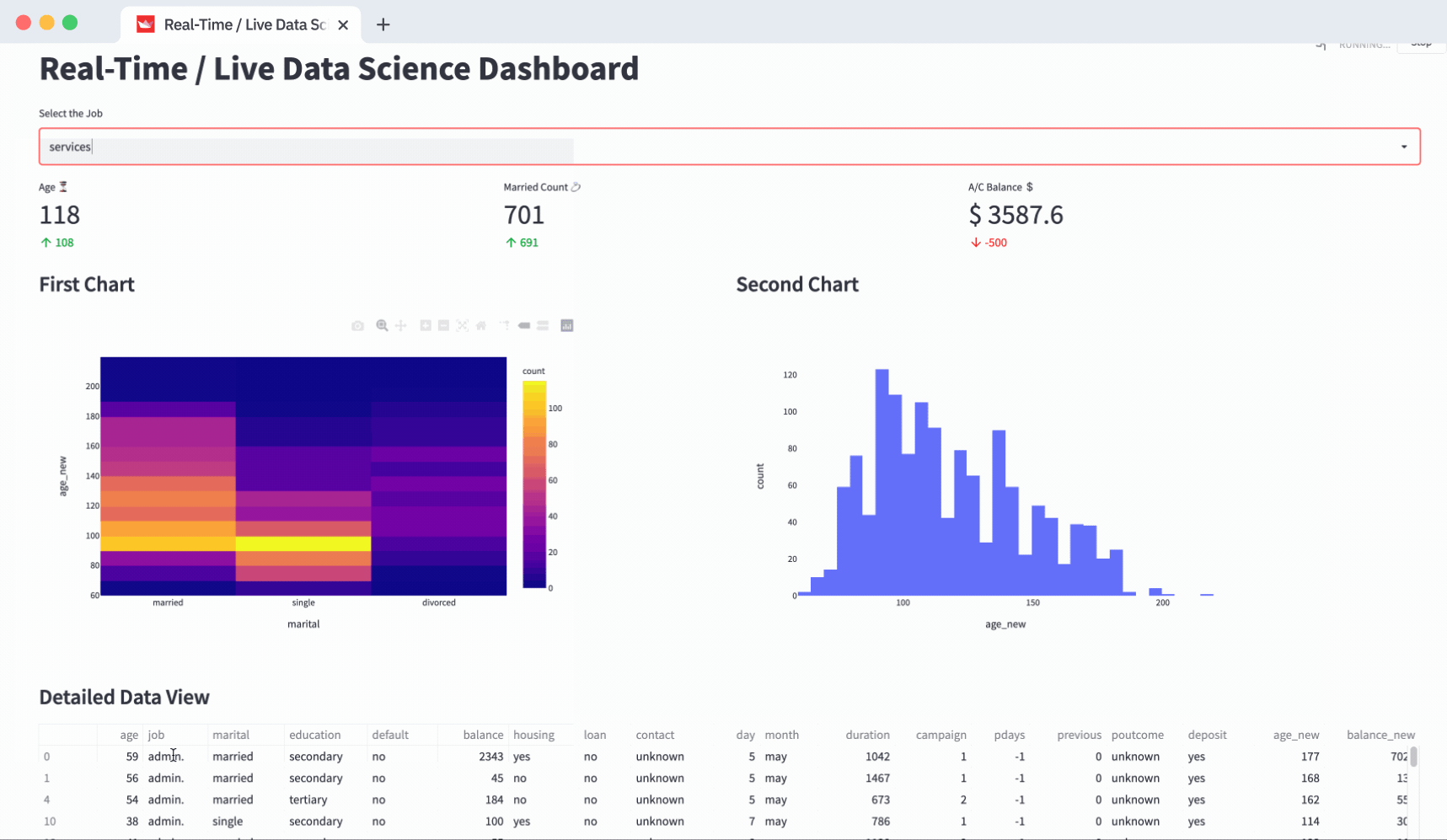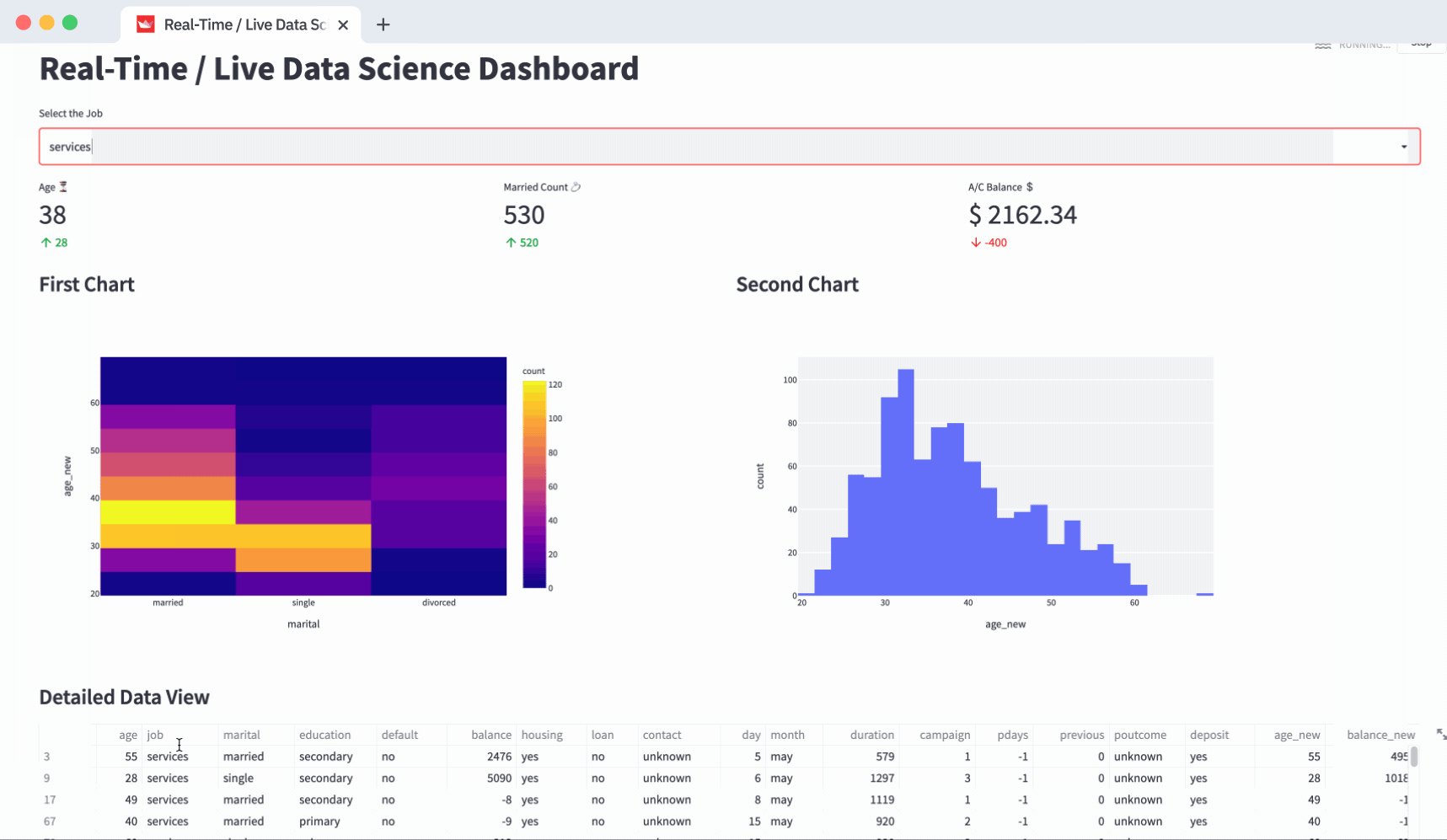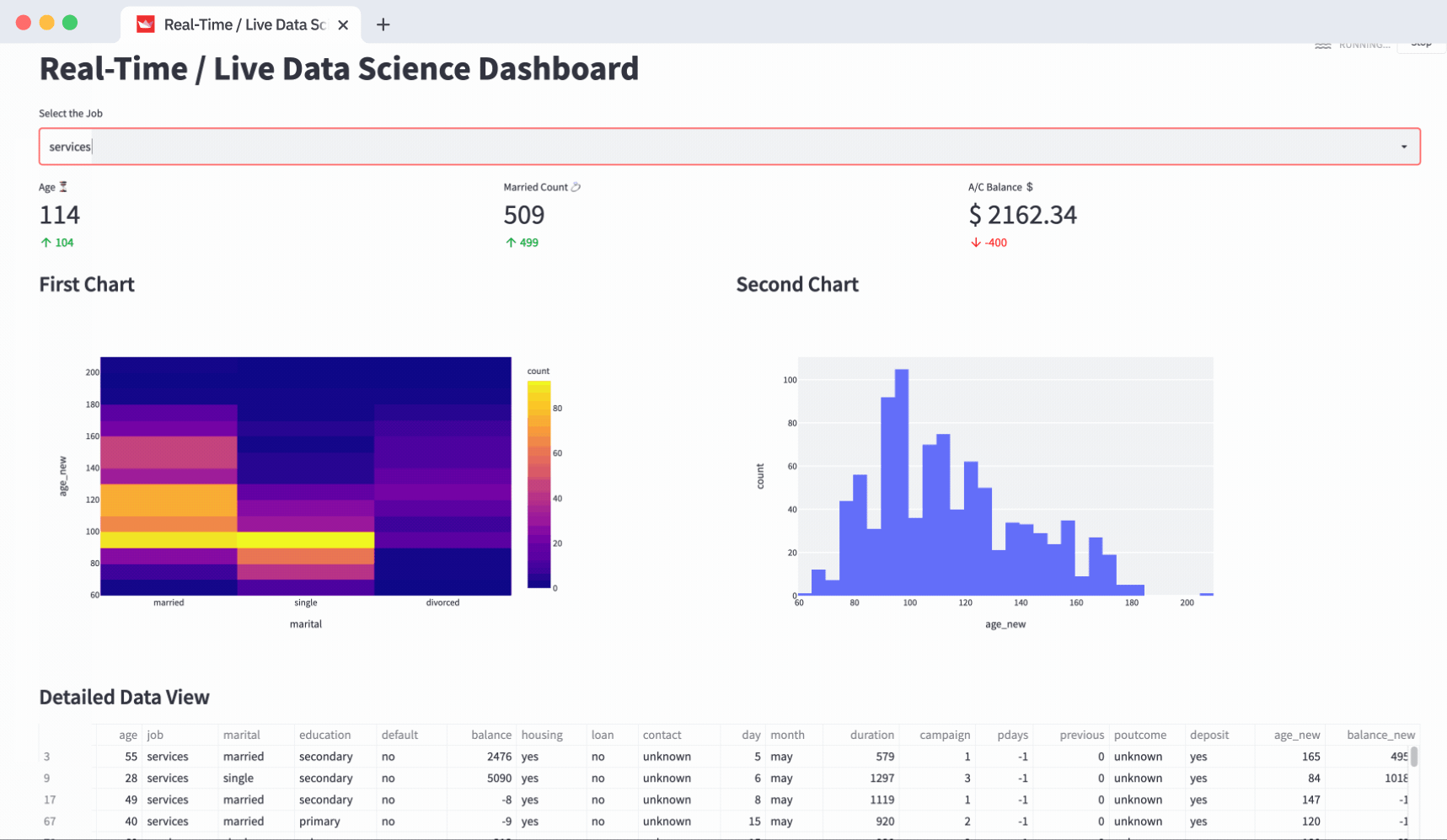
Building a Practical Dashboard: Step-by-Step
Let us walk through building a simple interactive sales dashboard using Streamlit as will be taught in a standard Data Analyst Course.
Step 1: Load and Prepare Data
Use Pandas to read and clean your dataset.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv(“sales.csv”)
df[‘Date’] = pd.to_datetime(df[‘Date’])
Step 2: Create Filters
Used to filter data by region or product category.
region = st.selectbox(“Select Region”, df[‘Region’].unique())
product = st.multiselect(“Select Product”, df[‘Product’].unique())
filtered_df = df[(df[‘Region’] == region) & (df[‘Product’].isin(product))]
Step 3: Add Charts
Visualise trends with Streamlit’s built-in chart functions.
st.line_chart(filtered_df.groupby(‘Date’)[‘Sales’].sum())
Step 4: Display KPIs
Show key performance indicators at a glance.
st.metric(“Total Sales”, f”${filtered_df[‘Sales’].sum():,.2f}”)
Users can readily generate custom views of the data with just a few clicks, making it easier to identify patterns, track goals, and make informed decisions.
Advantages Over Other Tools
While tools like Tableau and Power BI are widely used, Streamlit stands out for several reasons:
- Open Source & Free: Ideal for individuals and small teams with limited budgets.
- Custom Python Logic: Allows complete control over data transformations and calculations.
- Rapid Prototyping: Turn notebooks or scripts into apps in minutes.
- No Learning Curve: If you know Python, you can build dashboards—no web development skills are needed.
This simplicity and flexibility have made Streamlit a favourite among data professionals who want to move from analysis to application quickly.
Expanding Your Skill Set as a Data Analyst
In the evolving field of data analytics, simply knowing how to analyse data is no longer enough. The ability to present your findings effectively, especially through dashboards, is a crucial skill.
Completing a data course that includes practical modules on data visualisation and tools like Streamlit can be a valuable investment. Such courses help learners go beyond Excel and PowerPoint, teaching them how to turn static insights into interactive, decision-support tools. Through real-world projects, students also learn how to deploy these dashboards using platforms such as Streamlit Cloud, Heroku, or AWS.
These hands-on skills are not only impressive to employers but also essential for analysts looking to drive impact in modern organisations.
Best Practices for Building Streamlit Dashboards
Following are some practice tips for creating compelling and user-friendly dashboards:
- Keep it Simple: Avoid clutter and focus on key metrics.
- Use Clear Labelling: Ensure all filters, charts, and KPIs are clearly titled.
- Optimise Performance: For large datasets, consider caching results or sampling data.
- Add Explanations: Use markdown sections (st.markdown()) to explain trends or findings.
- Test Responsiveness: Ensure your dashboard functions smoothly across various devices and screen sizes.
Following these best practices ensures that your dashboard is not only functional but also intuitive and professional.
Conclusion
Interactive dashboards have become indispensable tools for modern data analytics, enabling users to explore data, discover insights, and make decisions—all in real-time. Streamlit provides an accessible, efficient, and powerful platform for building these dashboards using Python, eliminating the need for complex front-end development.
From simple data viewers to sophisticated analytics portals, Streamlit empowers data professionals to bridge the gap between analysis and action. For those looking to master such tools, a comprehensive Data Analytics Course in mumbai can provide the training and confidence needed to build impactful, production-ready dashboards.
In a world that increasingly values data-driven decision-making, the ability to create interactive, insightful dashboards is not just a nice-to-have—it is a career-defining skill.
Business Name: ExcelR- Data Science, Data Analytics, Business Analyst Course Training Mumbai
Address: Unit no. 302, 03rd Floor, Ashok Premises, Old Nagardas Rd, Nicolas Wadi Rd, Mogra Village, Gundavali Gaothan, Andheri E, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400069, Phone: 09108238354, Email: enquiry@excelr.com.




